self test for testicular torsion|how to diagnose testicular torsion : distribution Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. Ultrasound is the . WEBA FMU é uma instituição de ensino superior com mais de 100 cursos de graduação, pós-graduação, MBA e mestrado em diversas modalidades e unidades. Veja as vantagens, .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 13 de jan. de 2022 · Error. El resultado de la digestión debe ser igual al resultado de la desencripción del sello. Sistema desktop para generar .
A testicular self-exam (TSE) is a step-by-step method to check the appearance and feel of your testicles (testes). It’s important to be familiar with your testicles — and your body in general — so you can more easily notice changes or potential problems, including testicular cancer. Doctors often diagnose testicular torsion with a physical exam of the scrotum, testicles, abdomen and groin. Your doctor might also test your reflexes by lightly rubbing or . A testicular self-exam is an inspection of the appearance and feel of your testicles. You can do a testicular exam yourself, typically standing in front of a mirror. Routine . Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. Ultrasound is the .
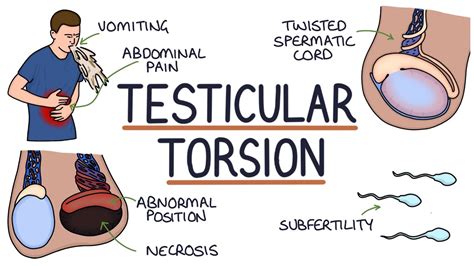
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding. Testicular torsion is the rotation of the testicle around the spermatic cord, which can obstruct its blood supply and lead to necrosis. Most often, testicular torsion affects young adolescents. The most common cause is .
Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which brings blood to the testicle from the abdomen. If the testicle rotates several times, blood flow to . Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord becomes twisted. This causes a restriction in blood flow to the testes, severe pain, and possibly permanent damage. Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, .
Investigations. The diagnosis of testicular torsion is a clinical one, therefore any suspected cases should be taken straight to theatre for scrotal exploration.. However, in cases with sufficient equipoise, Doppler ultrasound . Testicular torsion is most common between ages 12 and 18. Previous testicular torsion. If you've had testicular pain that went away without treatment (intermittent torsion and detorsion), it's likely to occur again. The more frequent the bouts of pain, the higher the risk of testicular damage. Family history of testicular torsion.
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. [3] The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. [1] The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. [1] [2] In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become .What is a testicular self-exam? A testicular self-exam (TSE) is a step-by-step method to check the appearance and feel of your testicles (testes). It’s important to be familiar with your testicles — and your body in general — so you can more easily notice changes or potential problems, including testicular cancer.A healthcare provider may also conduct a testicular exam during . Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates around the spermatic cord, which provides blood to the scrotum (a bag of skin that contains the testicles). Testicular torsion typically affects adolescents, although it can occur at all ages, including newborns and older adults. . Additional diagnostic methods include urine tests to exclude .
Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of .Testicular torsion is an emergency condition. It happens when the spermatic cord, which provides blood flow to the testicle, rotates and becomes twisted. The twisting cuts off the testicle's blood supply and causes sudden pain and swelling. Testicular torsion requires surgery right away to save the .A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes).
Testicular cancer is the most common cancer in males ages 15-34, although many cases fall outside these parameters. There is one male diagnosed every hour with testicular cancer. The good news is that detecting Testicular Cancer can often be done through a simple Testicular Cancer Self Exam (TSE). You might get one or more of these tests to diagnose testicular torsion: Urine test (checks for an infection) An imaging test of your scrotum, usually an ultrasound that uses sound waves to check . Testicular torsion, or twisted testicle, can be extremely painful. . A healthcare professional may also test the patient’s cremasteric reflex, which is highly effective in helping diagnose . Doctors agree that men should routinely perform a testicular self-examination. Learn about how often you should do it, how to do it properly, and spot warning signs that may warrant a visit to a .
Testicular torsion can occur at any age, although it is more common in the first year of life and at puberty (peak age being 12-18 years). Testicular torsion can even occur before birth (during the prenatal period). Left testicle torsion is more common than right testicle torsion. The exact cause of testicular torsion is not known.
How is testicular torsion diagnosed? Diagnosis entails a physical examination and a complete medical history. A prompt diagnosis is imperative because prolonged testicular torsion may cause irreversible damage to the testes. Other diagnostic tests may be done, but there is no test that diagnoses testicular torsion accurately all the time. Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. The most common symptom is acute testicular pain and the most common underlying cause, a bell-clapper deformity. The diagnosis is often made clinically but if it is in doubt, an ultrasound is helpful in confirming the diagnosis. .
You're definitely suffering from torsion 😅 just kidding. Torsion causes isquemia and it's an acute onset of pain you won't forget, diagnosed through eco-doppler silence + clinical manifestation. You might have a varicocele or a small inguinal herniation? Get yourself checked out. Our age is the most affected by testicular cancer..May have previous similar intermittent, self-resolving episodes; May present after scrotal trauma with persistent pain; May present as lower abd pain; thus, inquire specifically about scrotal pain in males with abd pain . ↑ Barbosa, JA, et al. Development of initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in children . Testicular torsion can be extremely painful and is an emergency situation. It happens when the testical cord that carries blood to the testicles twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicles. . Self-diagnose with our free Buoy Assistant if you answer yes on any of these questions. Testicular torsion in children. Younger children or .
testicular torsion signs on examination
In summary, diagnosing testicular torsion involves physical examinations, imaging tests, and prompt action. Delayed treatment can have severe consequences, including testicular loss and infertility. Treatment options include manual detorsion and surgical intervention, with the choice depending on the specific circumstances of the case. Answer: Testicular torsion 1-15. Epidemiology. Bimodal incidence: 1 st year of life and teenage years (12-18 years) 1,2; Rare case reports of men age > 40 years with cases of testicular torsion 1,2; 50% of patients with testicular torsion have a previous episode of torsion that spontaneously resolved 3; Testicular pain accounts for 1% of ED visits annually 1 .No way it’s a testicular torsion right? . Had my younger self read this post, maybe I'd still have two balls and one less traumatic experience. So if you're reading this and you ever wake up feeling like you've been kicked in the nuts, please see a doctor immediately. It is not normal and even if you puke the whole way there, it will .
Testicular cancer is one of the most common cancers among young men, yet many are unfamiliar with the disease and how easily they can play a role in detecting it.To help, testicular cancer expert Nirmish Singla from the Brady Urological Institute explains how — and why — you should perform regular self-checks.. Why should I check my testicles for cancer?
About testicular torsion Testicular torsion is something that 1 in 4000 men under the age of 25 experience every year. . Other tests that can be considered to look for other conditions include Ultrasound and urine or blood tests. . The Urology Foundation is calling for changes to the curriculum to include education on testicular health and . In this video we cover key things that you need to know about a TESTICULAR TORSION. Testicular torsion occurs when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic. What is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion happens when testicles rotate and the spermatic cord becomes twisted. The spermatic cord supports the testes in the scrotum. When the cord twists, the blood supply to the testicle is cut off. If it’s not treated quickly, the testicle can die and will have to be removed.Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of
This is called testicular torsion. If testicular torsion occurs, it requires urgent medical attention. What causes testicular torsion and who is at risk? Testicular torsion can happen to boys and men of any age, but most cases occur in .
reliable change index impact test
renogy solar panel impact test
15 de set. de 2023 · Em resumo, “Não Mendigue Afeto: O Poder de Se Amar” é um guia essencial para todas as mulheres que desejam desenvolver o amor próprio, .
self test for testicular torsion|how to diagnose testicular torsion